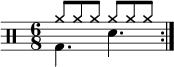Month: February 2019
Tchaikovsky by Janine Jansen & Friends – Souvenir de Florence
HOW TO READ ANY RHYTHM
ubuntu – how to disable LibreOffice Impress to use multiple display?
You need to disable the presenter console:
- Go to Tools > Options;
- Then choose Open Office Impress > General in the left menu;
- Then under the Start Presentation section on the right side;
- uncheck the box with Presenter Screen.
Source: ubuntu – how to disable LibreOffice Impress to use multiple display? – Stack Overflow
Gothenburg Concert Hall
Chi mai fra gl’inni e i plausi. Brussels. 2004 (from Verdi’s Aida) – YouTube
Top TEN Things I Wish I Knew BEFORE Becoming A Musician
How To Develop The World’s Greatest Ear Part 1
Ear Training – Chromatic Solfege
Solfège
In music, solfège (UK: /ˈsɒlfɛdʒ/, US: /sɒlˈfɛʒ/; French: [sɔlfɛʒ]) or solfeggio (/sɒlˈfɛdʒioʊ/; Italian: [solˈfeddʒo]), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a music education method used to teach pitch and sight singing of Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, and though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, the systems used in other music cultures such as swara, durar mufaṣṣalāt and Jianpu are discussed in their respective articles.
Syllables are assigned to the notes of the scale and enable the musician to audiate, or mentally hear, the pitches of a piece of music which he or she is seeing for the first time and then to sing them aloud. Through the Renaissance (and much later in some shapenotepublications) various interlocking 4, 5 and 6-note systems were employed to cover the octave. The tonic sol-fa method popularized the seven syllables commonly used in English-speaking countries: do (or doh in tonic sol-fa), re, mi, fa, so(l), la, and si (or ti), see below).
There are two current ways of applying solfège: 1) fixed do, where the syllables are always tied to specific pitches (e.g. “do” is always “C-natural”) and 2) movable do, where the syllables are assigned to scale degrees (“do” is always the first degree of the major scale).
Understanding the Fundamentals of Music
Metre (music)
Compound metre (or compound time), is a metre in which each beat of the bar divides naturally into three equal parts. That is, each beat contains a triple pulse (Latham 2002a). The top number in the time signature will be 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 24, etc.
Compound metres are written with a time signature that shows the number of divisions of beats in each bar as opposed to the number of beats.