Month: July 2017
Charles Babbage
Notation for differentiation
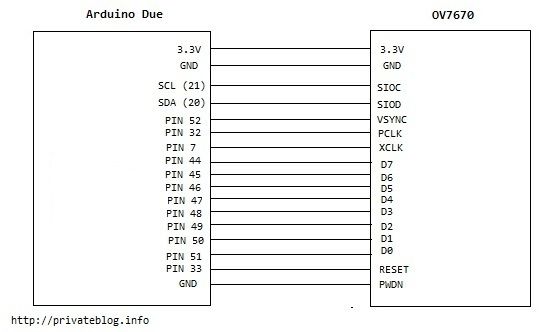
How to Connect OV7670 to Arduino Due: 6 Steps (with Pictures)
This instruction is a quick translation for an instruction in Russian available at
http://privateblog.info/arduino-due-i-kamera-ov7670-primer-ispolzovaniya/
Connection of OV7670 to Arduino Due is easier than to Arduino Uno: lower operation voltage – only 3V, higher internal speed, more memory and more contacts on the board.
Source: How to Connect OV7670 to Arduino Due: 6 Steps (with Pictures)
How does P2P IP camera work? | Technology News
HOW DOES P2P IP CAMERA WORK?Just input the Device ID and password, without network configuration, your IP camera can connect to network for remotely monitoring. How does it work? The simple answer is “Peer to Peer” or P2P technology. P2P technology can allow camera communicates with other network devices without complicated network settings. Today, we are going to discuss it in this article.
Building a low cost wifi camera – Johan Kanflo
Sometime ago I came across the Arducam Mini which is quite a nice camera module from UCTronics. It is a small PCB with a two megapixel OmniVision OV2640 sensor, an interchangeable lens and an FPGA to do the heavy lifting of image processing and JPEG encoding. Priced at around 24 Euros (lens included) you can easily buy a few without hurting your wallet and combined with an ESP8266 you can build quite a low cost wifi camera. Or several. Because designing and building PCBs is both fun and inexpensive I designed a board to go with the ESP8266/Arducam Mini combo, aptly named the Esparducam. And uniquely named too, try googeling for “esparducam“. Heck, even the domain name is available at the time of writing
ESP8266 WIFI Camera | Arduino Based Camera
ArduCAM now released a world smallest low cost ESP8266 WIFI IoT camera kit based on ArduCAM-Mini-2MP-V2 and ArduCAM-ESP8266-Nano module. User can implement a 2MP WIFI camera using HTTP or Websocket protocol on ESP8266, and the camera can be acted as an AP and mobile phone/PC can connect to the camera directly or acted as a Station which connected to the home router. The kit can capture 2MP full resolution JPEG still image, even stream low resolution at fairly frame rate video over network or directly save to local SD/TF card. The kit is suitable for portable application, it can be powered from micro-USB or using battery and has build in lithium battery charging circuits. The kit can also be used separately, it is almost identical to standard alone ArduCAM-Mini-2MP camera and ESP8266-12F module. Continue reading “World Smallest ESP8266 WIFI Camera” »
Kiri Te Kanawa-Chi il bel sogno di Doretta – YouTube
De Morgan’s laws
Augmented third
In classical music from Western culture, an augmented third (![]() Play ) is an interval of fivesemitones. It may be produced by widening a major third by a chromatic semitone.[1][3] For instance, the interval from C to E is a major third, four semitones wide, and both the intervals from C♭ to E, and from C to E♯ are augmented thirds, spanning five semitones. Being augmented, it is considered a dissonant interval.
Play ) is an interval of fivesemitones. It may be produced by widening a major third by a chromatic semitone.[1][3] For instance, the interval from C to E is a major third, four semitones wide, and both the intervals from C♭ to E, and from C to E♯ are augmented thirds, spanning five semitones. Being augmented, it is considered a dissonant interval.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Augmented_third
Major third
In classical music from Western culture, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major third (![]() Play ) is a third spanning four semitones. Along with the minor third, the major third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is qualified as major because it is the larger of the two: the major third spans four semitones, the minor third three. For example, the interval from C to E is a major third, as the note E lies four semitones above C, and there are three staff positions from C to E. Diminished andaugmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five).
Play ) is a third spanning four semitones. Along with the minor third, the major third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is qualified as major because it is the larger of the two: the major third spans four semitones, the minor third three. For example, the interval from C to E is a major third, as the note E lies four semitones above C, and there are three staff positions from C to E. Diminished andaugmented thirds span the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five).
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Major_third
Minor third
In the music theory of Western culture, a minor third is a musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing threestaff positions (see: interval number). The minor third is one of two commonly occurring thirds. It is called minor because it is the smaller of the two: the major third spans an additional semitone. For example, the interval from A to C is a minor third, as the note C lies three semitones above A, and (coincidentally) there are three staff positions from A to C. Diminished and augmented thirdsspan the same number of staff positions, but consist of a different number of semitones (two and five). The minor third is a skip melodically.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minor_third