In Western music, the adjectives major and minor can describe a musical composition,movement, section, scale, key, chord, or interval.
Major and minor are frequently referred to in the titles of classical compositions, especially in reference to the key of a piece.
Contents
Intervals and chords
Major and minor third in a major chord: major third ‘M’ on bottom, minor third ‘m’ on top. ![]() Play
Play
Relative tonic chords on C and A. ![]() Play
Play
Parallel tonic chords on C
Major chord
Minor chord
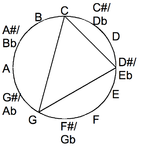
The difference between the major and minor chord may be seen if they are drawn in chromatic circle.
With regard to intervals, the words major and minor just mean large and small, so a major third is a wider interval, and a minor third a relatively narrow one. The intervals of the second, third, sixth, and seventh (and compound intervals based on them) may be major or minor.
The other uses of major and minor, in general, refer to musical structures containing major thirds or minor thirds. A major scale is one whose third degree is a major third above thetonic, while a minor scale has a minor third degree. A major chord or major triad, similarly, contains a major third above theroot, whereas a minor chord or minor triad contains a minor third above the root. In Western music, a minor chord, in comparison, “sounds darker than a major