Music
Additive rhythm and divisive rhythm
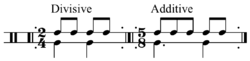
In music, the terms additive and divisive are used to distinguish two types of both rhythm and meter:
- A divisive (or, alternately, multiplicative) rhythm is a rhythm in which a larger period of time is divided into smaller rhythmic units or, conversely, some integer unit is regularly multiplied into larger, equal units.
- This can be contrasted with additive rhythm, in which larger periods of time are constructed by concatenating (joining end to end) a series of units into larger units of unequal length, such as a 5
8 meter produced by the regular alternation of 2
8 and 3
8 (London 2001, §I.8).
When applied to meters, the terms perfect and imperfect are sometimes used as the equivalents of divisive and additive, respectively (Read 1969, 150).
For example, 4 may be evenly divided by 2 or reached by adding 2 + 2. In contrast, 5 is only evenly divisible by 5 and 1 and may be reached by adding 2 or 3. Thus, 4
8 (or, more commonly, 2
4) is divisive while 5
8 is additive.
Additive meter – Definition
Source: Additive meter – Definition (Artopium’s Music Dictionary)
Yo-Yo Ma: Tchaikovsky “Andante Cantabile” (live) – YouTube
Mode (music)
Mode Tonic relative
to major scaleInterval sequence Example Ionian I W-W-H-W-W-W-H C-D-E-F-G-A-B-C Dorian II W-H-W-W-W-H-W D-E-F-G-A-B-C-D Phrygian III H-W-W-W-H-W-W E-F-G-A-B-C-D-E Lydian IV W-W-W-H-W-W-H F-G-A-B-C-D-E-F Mixolydian V W-W-H-W-W-H-W G-A-B-C-D-E-F-G Aeolian VI W-H-W-W-H-W-W A-B-C-D-E-F-G-A Locrian VII H-W-W-H-W-W-W B-C-D-E-F-G-A-B
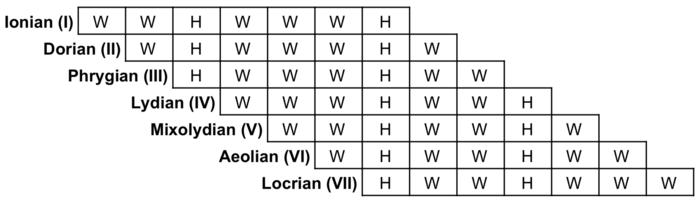
Source: Mode (music) – Wikipedia
E minor
E minor is a minor scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F♯, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature has one sharp. Its relative major is G major and its parallel major is E major.
The E natural minor scale is:
Source: E minor – Wikipedia
Anne Sophie-Mutter – Mendelssohn Violin Concerto in E minor, Op.64 – Kurt Masur – YouTube
Clémentine Margaine
A minor
Source: A minor – Wikipedia
Schumann – Piano Concerto in A minor, Op. 54 (Sheet Music)
Schumann Piano Concerto, in A minor, OP. 54 Martha Argerich & Riccardo Chailly – YouTube
Tempo rubato
Tempo rubato ([ˈtɛmpo ruˈbaːto]; “free in the presentation”, Italian for “stolen time”) is a musical term referring to expressive and rhythmic freedom by a slight speeding up and then slowing down of the tempo of a piece at the discretion of the soloist or the conductor. Rubato is an expressive shaping of music that is a part of phrasing.[1]
While rubato is often loosely taken to mean playing with expressive and rhythmic freedom, it was traditionally used specifically in the context of expression by speeding up and then slowing down the tempo. In the past, expressive and free playing (beyond only rubato) was often associated with the terms “ad libitum.” Rubato, even when not notated, is often used liberally by musicians; e.g. singers frequently use it intuitively to let the tempo of the melody expressively shift slightly and freely above that of the accompaniment. This intuitive shifting leads to rubato’s main effect: to make music sound expressive and natural. Frédéric Chopin is often mentioned in context with rubato (see Chopin’s technique and performance style).
Source: Tempo rubato – Wikipedia