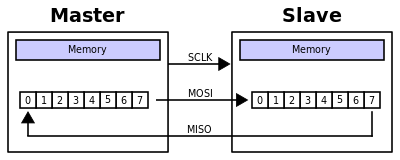
The Serial Peripheral Interface bus (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the late eighties and has become a de facto standard. Typical applications include Secure Digital cards and liquid crystal displays.
SPI devices communicate in full duplex mode using a master-slave architecture with a single master. The master device originates the frame for reading and writing. Multiple slave devices are supported through selection with individual slave select (SS) lines.
Sometimes SPI is called a four-wire serial bus, contrasting with three-, two-, and one-wire serial buses. The SPI may be accurately described as a synchronous serial interface,[1] but it is different from the Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) protocol, which is also a four-wire synchronous serial communication protocol. But SSI Protocol employs differential signaling and provides only a single simplex communication channel.