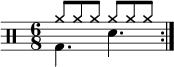In music, a tuplet (also irrational rhythm or groupings, artificial division or groupings, abnormal divisions, irregular rhythm, gruppetto, extra-metric groupings, or, rarely, contrametric rhythm) is “any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the time-signature (e.g., triplets, duplets, etc.)” (Humphries 2002, 266). This is indicated by a number (or sometimes two), indicating the fraction involved. The notes involved are also often grouped with a bracket or (in older notation) a slur.
Source: Tuplet – Wikipedia